NMR Analyzer Application on Aquatic Products Quality Monitoring during Storage
본문
NMR Analyzer Applications overview:
Moisture is the main component of many foods, each food has a specific moisture content that present in appropriate quantities and specific orientation. Moisture content has a lot of influence on the food structure, appearance and susceptibility to corruption. In addition, NMR analyzer has been widely used in the proton study. In 1950, the USA have already begun to study the hydration of the food by NMR techniques. Recently, domestic NMR study in the water phase, distribution and migration of the food moisture, etc. reflecting the changes of the food ingredients such as proteins, showing the process of the changes in food quality.
Low field NMR applications:
- Water migration and quality monitoring during the aquatic products storage;
- Lean meats and fat of living seafood such as fish body composition testing;
NMR Application Case 1: the changes of shrimps NMR relaxation spectra in 4℃ storage
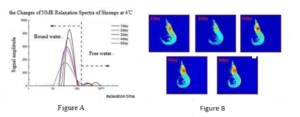
Fig 1:the changes of shrimps NMR relaxation spectra in 4℃ storage
(A) Changes of nuclear magnetic resonance T2 relaxation spectrum for shrimp 4 ℃ storage
(B) MRI proton density storage time;
According to literature [1], bound water is the water between muscle fibers, located in the gap of the protein space network structure; free water exists outside of the muscle fiber bundles. In the storage process, bound water content gradually reduced, free water content decreased firstly and then increased. This is mainly due to that the water located in shrimp gill and the body surface constantly evaporate in the prime of the storage, free water gradually reduced.
In the late, the damage of the protein spatial structure lead to the bound water’s decline and the changes of the cell permeability and fluid exudation, including bound water and free water’s reduction, muscle relaxation. That all match the damage of the protein structures in the storage process;
Figure B shows that in magnetic resonance images, the brighter the image, the greater the hydrogen protons density and the stronger the moisture movement. Storage during the process of 1-5 d, shrimp images’ brightness dimed after the first light, indicate that water content decreased firstly and then increased, water movement increases and the microorganism are more active. Overall, Shrimp corruption start from the head, so the head signal lights in the image.
NMR Application case 2 : Cod quality monitoring in -10 ℃ storage process;
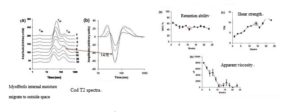
- The cod in -10 ℃ storage, the moisture in the myofibrils interior and gaps transfer to the outside space, leading the bound water content decreases and the free water content increased. During the 10-14 weeks, the free water content and shear stress achieved maximum, while the apparent viscosity and water holding capacity meet the minimum at the same time.
- Correlation analysis showed that during the whole storage process, apparent viscosity, shear forces, bound water and free water content showed a good exponent correlation. Test results show that the low-field NMR can be used to monitor the quality of cod during storage, and predict shelf life of aquatic products. (literature [2])
NMR Application case 3: shrimp meat drying process moisture distribution and migration
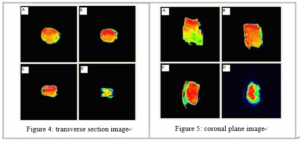
Figure 4: transverse section proton density-weighted images at different point-in-time
Figure 5: coronal plane proton density-weighted images at different point-in-time
(A: Initial moments; B: Drying for 10 min; C: Drying for 20 min; D: Drying for 30 min)
- In figure 4 and figure 5, the color represents the signal strength. The stronger the red signal, the greater the proton density. The larger the blue signals, the smaller the proton density. Magnetic resonance imaging can evident different drying period water distribution and changes clearly.
- During the drying process, shrimp meat volume reduced significantly, the water distribute uneven in different regions. Through an analysis of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging signal in different regions to further study the area drying rate, providing a quick and intuitive way for the determining of the drying process and shrimp meat quality research.


 TD-NMR/MRI
TD-NMR/MRI